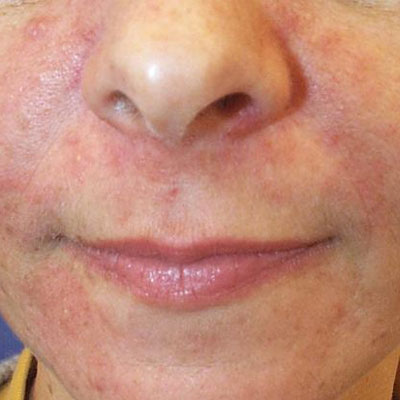
Rosacea occurs more commonly in those of Northern European descent. Rosacea is chronic, usually lasting for several years going through periods of flares and remission. Many people get redness, bumps, or both. The redness is often triggered by factors outlined below and often progressively worsens. In many people, the bumps are small and look like acne, except you usually can’t get anything from squeezing them. Ocular rosacea is an often under-diagnosed eyelid condition associated with itchy, dry feeling eyes, frequent styes, and red eyelids.
Trigger factors for Rosacea
W.C. Fields had horrible rosacea, as well as an unfortunate drinking habit that led many to believe that anyone with rosacea was an alcoholic. Rosacea is not caused by alcohol, but alcohol can enhance the redness in some patients.
- Caffeine also does not cause it, but any hot beverage, including coffee, can cause flushing and more redness (as can any spicy food). Eliminating these or any other foods from your diet will minimize flushing if they act as triggers in you, but otherwise won’t make your rosacea go away.
- Sun exposure also does not cause rosacea, but can cause flare ups.
- Finally, emotion can trigger flushing, as can changes in temperature.
Treatment for Rosacea
Presently, there is no cure for this disease, but it can be managed. A variety of oral antibiotics usually produce the fastest, most reliable results, but there are also several topical medicines that may be effective with less risk, as well as laser treatments that help with redness.
Oral medicines
Doxycycline, tetracycline, minocycline, erythromycin, metronidazole, and azithromycin have all been effective. 100-200 mg daily of doxycycline is a typical starting point. Once bumps and pustules have cleared (often 2-4 weeks), the medicine can be stopped. Many patients will then stay in remission, but for those who don’t, treatment may be continued. Isotretinoin (Accutane), usually for 5 months, can be used when all else fails.
Topical treatments are great for maintenance of Rosacea
Metronidazole, Sulfacetamide/sulfur lotion, azeleic acid, clindamycin and others are all useful topical agents for more mild rosacea or for maintenance after achieving control with oral antibiotics.
Sunscreen is critical for Rosacea patients
It is usually worthwhile for rosacea patients to include daily sunscreen in their regimen year round. I recommend SPF 30 in the winter and 50 in the summer. This can be found as part of many moisturizers. For men, an aftershave lotion with sunscreen can be applied all over the face for a 1-step solution.
Laser treatments for Rosacea
Vbeam laser is very effective at treating persistent redness and dilated veins. It is seen as purely cosmetic by insurance companies, but is relatively affordable, produces lasting results and is quite safe. Several treatments are often required, depending on how much redness there is to remove. You will still have rosacea and a tendency to become red again with time, but if you treat your rosacea and use sunscreen diligently, you can usually get several years of benefit from laser treatment.